Note
Go to the end to download the full example as a Python script or as a Jupyter notebook..
Add points with features#
Display a points layer on top of an image layer using the add_points and
add_image APIs
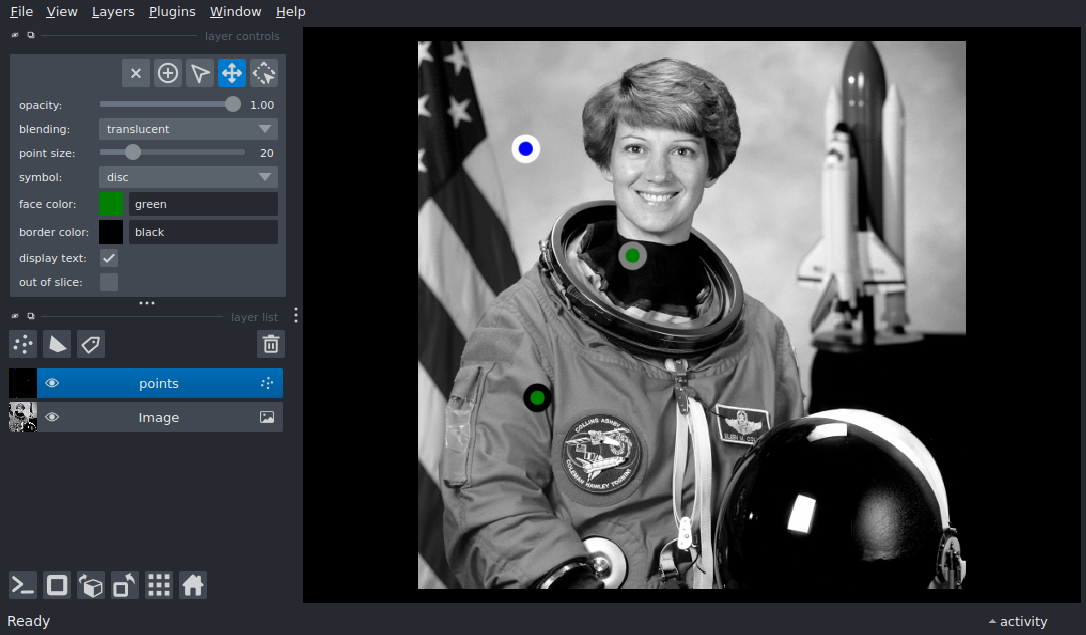
import numpy as np
from skimage import data
from skimage.color import rgb2gray
import napari
# add the image
viewer = napari.Viewer()
layer = viewer.add_image(rgb2gray(data.astronaut()))
# add the points
points = np.array([[100, 100], [200, 200], [333, 111]])
# create features for each point
features = {
'confidence': np.array([1, 0.5, 0]),
'good_point': np.array([True, False, False])
}
# define the color cycle for the face_color annotation
face_color_cycle = ['blue', 'green']
# create a points layer where the face_color is set by the good_point feature
# and the border_color is set via a color map (grayscale) on the confidence
# feature.
points_layer = viewer.add_points(
points,
features=features,
size=20,
border_width=7,
border_width_is_relative=False,
border_color='confidence',
border_colormap='gray',
face_color='good_point',
face_color_cycle=face_color_cycle
)
# set the border_color mode to colormap
points_layer.border_color_mode = 'colormap'
# bind a function to toggle the good_point annotation of the selected points
@viewer.bind_key('t')
def toggle_point_annotation(viewer):
selected_points = list(points_layer.selected_data)
if len(selected_points) > 0:
good_point = points_layer.features['good_point']
good_point[selected_points] = ~good_point[selected_points]
points_layer.features['good_point'] = good_point
# we need to manually refresh since we did not use the Points.features
# setter to avoid changing the color map if all points get toggled to
# the same class, we set update_colors=False (only re-colors the point
# using the previously-determined color mapping).
points_layer.refresh_colors(update_color_mapping=False)
if __name__ == '__main__':
napari.run()