Note
Go to the end to download the full example as a Python script or as a Jupyter notebook..
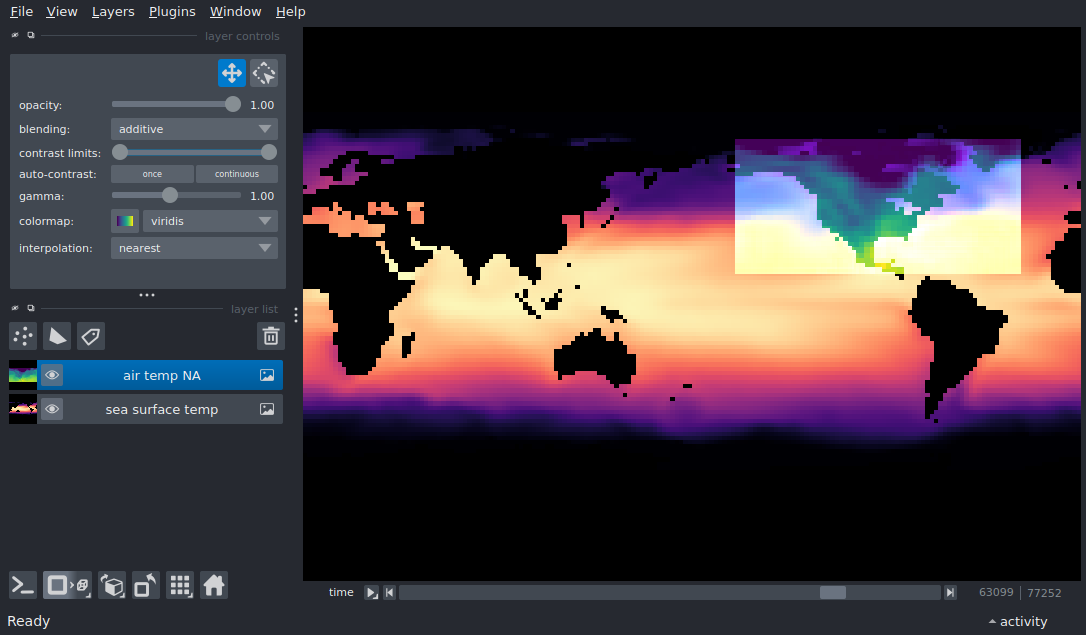
Displaying xarray data in napari#
This example shows how to view xarray datasets in napari, including scale and translation information.
Currently, napari cannot display irregularly-sampled data, so the code assumes that the data indices are regularly spaced. If your indices are irregular, use xarray.Dataset.interp to create a regularly-spaced version before displaying it in napari.
import numpy as np
import xarray as xr
import napari
# open the xarray global sea surface temperature (40MB) and North America
# air temperature (30MB) datasets
sst = xr.tutorial.open_dataset('ersstv5')
airtemp = xr.tutorial.open_dataset('air_temperature')
def get_scale_translate(dataset, array_name):
"""Get the translate/offset and scale parameters for an xarray dataset.
This code assumes that the dataset is regularly spaced. You should
interpolate your data if it is sampled at irregular spaces.
Parameters
----------
dataset : xr.Dataset
The dataset containing the array to be displayed.
array_name : str
The name of the xarray DataArray within `dataset` to be displayed in
napari.
Returns
-------
param_dict : dict[str, list[float]]
The scale and translate parameters computed from the xarray dimension
indices.
"""
array = getattr(dataset, array_name)
if array is None:
raise ValueError(f'{dataset} has no array with name {array_name}')
dims = [getattr(dataset, dim) for dim in array.dims]
translate = [float(d[0]) for d in dims]
scale = [float(d[1] - d[0]) for d in dims]
return {'scale': scale, 'translate': translate}
# Show the raw (not resampled) model data
viewer, sst_layer = napari.imshow(
sst.sst,
name='sea surface temp',
**get_scale_translate(sst, 'sst'),
colormap='magma',
)
viewer.dims.axis_labels = sst.sst.dims
air_layer = viewer.add_image(
airtemp.air,
name='air temp NA',
**get_scale_translate(airtemp, 'air'),
colormap='viridis',
blending='additive',
contrast_limits=(-23 + 273, 32 + 273), # data are in degrees Kelvin
)
# set a time that overlaps both datasets
viewer.dims.set_point(0, np.datetime64('2013-03-10T18:00:00.000000000'))
# latitude goes from -90 (south, down) to 90 (north, up),
# so we make sure that the camera vertical axis points up.
viewer.camera.orientation2d = ('up', 'right')
# fill the frame
viewer.reset_view(margin=0)
if __name__ == '__main__':
napari.run()