Preferences#
napari settings#
napari provides persistent settings that are stored on a per environment basis. This means that if you have multiple Python environments, each with a napari installation (e.g. different versions), the napari in each environment will have its own set of stored preferences. So, for example, you could have an environment where napari always uses the Light theme and another one where napari always uses the Dark theme.
A wide range of settings are available, organized into sections, and described in more detail below.
Where settings are stored#
Settings are stored in a settings.yaml file and napari uses appdirs
to determine the save location: the platform-specific user configuration directory.
You can check where a napari installation has stored settings by looking for “Settings path” in the output of:
napari --info
Resetting settings to defaults using the command line (CLI)#
Sometimes, for example due to a version change, an issue with the stored settings can prevent napari from launching or cause other issues. In those cases, it can be useful to reset the settings to the defaults from the command line. To reset all napari settings to the default values:
napari --reset
Programmatic access to the settings#
Settings are managed by getting the global settings object and modifying settings:
from napari.settings import get_settings
settings = get_settings()
# then modify... e.g:
settings.appearance.theme = 'dark'
You can get more information about individual settings, their types, and default values in each of the settings section descriptions below.
The Preferences dialog#
napari provides a Preferences dialog to manage the settings using a graphical user interface (GUI). Importantly, this dialog also allows you to customize napari keyboard shortcuts (keybindings).
On Windows and Linux, the Preferences dialog can be accessed in the File menu. On macOS, it can be accessed in the napari menu.
The settings are grouped by sections that are accessible in a list on the left side of the dialog.
Application Settings#
Main application settings.
More details on the individual Application settings
Brush size on mouse move modifiers
Modifiers to activate changing the brush size by moving the mouse.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.application.brush_size_on_mouse_move_modifiers.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPLICATION_BRUSH_SIZE_ON_MOUSE_MOVE_MODIFIERSType:
BrushSizeOnMouseModifiersDefault:
<BrushSizeOnMouseModifiers.ALT: 'Alt'>.
Confirm window or application closing
Ask for confirmation before closing a napari window or application (all napari windows).
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.application.confirm_close_window.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPLICATION_CONFIRM_CLOSE_WINDOWType:
boolDefault:
True.
Console notification level
Select the notification level for the console.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.application.console_notification_level.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPLICATION_CONSOLE_NOTIFICATION_LEVELType:
NotificationSeverityDefault:
<NotificationSeverity.NONE: 'none'>.
Dask cache
Settings for dask cache (does not work with distributed arrays)
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.application.dask.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPLICATION_DASKType:
DaskSettingsDefault:
DaskSettings(enabled=True, cache=4.193072128).
Depth Axis Orientation
Orientation of the depth axis in 3D view. Default is “Towards”; <0.6.0 was “Away”.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.application.depth_axis_orientation.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPLICATION_DEPTH_AXIS_ORIENTATIONType:
DepthAxisOrientationDefault:
<DepthAxisOrientation.TOWARDS: 'towards'>.
Grid Height
Number of rows in the grid.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.application.grid_height.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPLICATION_GRID_HEIGHTType:
ConstrainedIntValueDefault:
-1.
Grid Spacing
The amount of spacing inbetween grid viewboxes. If between 0 and 1, it is interpreted as a proportion of the size of the viewboxes. If equal or greater than 1, it is interpreted as screen pixels.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.application.grid_spacing.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPLICATION_GRID_SPACINGType:
ConstrainedFloatValueDefault:
0.
Grid Stride
Number of layers to place in each grid viewbox before moving on to the next viewbox. A negative stride will cause the order in which the layers are placed in the grid to be reversed. 0 is not a valid entry.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.application.grid_stride.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPLICATION_GRID_STRIDEType:
ConstrainedIntValueDefault:
1.
Grid Width
Number of columns in the grid.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.application.grid_width.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPLICATION_GRID_WIDTHType:
ConstrainedIntValueDefault:
-1.
GUI notification level
Select the notification level for the user interface.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.application.gui_notification_level.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPLICATION_GUI_NOTIFICATION_LEVELType:
NotificationSeverityDefault:
<NotificationSeverity.INFO: 'info'>.
Delay to treat button as hold in seconds
This affects certain actions where a short press and a long press have different behaviors, such as changing the mode of a layer permanently or only during the long press.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.application.hold_button_delay.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPLICATION_HOLD_BUTTON_DELAYType:
floatDefault:
0.5.
Horizontal Axis Orientation
Orientation of the horizontal axis in 2D and 3D view. Default is “Right”.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.application.horizontal_axis_orientation.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPLICATION_HORIZONTAL_AXIS_ORIENTATIONType:
HorizontalAxisOrientationDefault:
<HorizontalAxisOrientation.RIGHT: 'right'>.
Language
Select the display language for the user interface.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.application.language.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPLICATION_LANGUAGEType:
LanguageDefault:
'en'.
New labels data type
data type for labels layers created with the “new labels” button.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.application.new_labels_dtype.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPLICATION_NEW_LABELS_DTYPEType:
LabelDTypesDefault:
<LabelDTypes.uint8: 'uint8'>.
Playback frames per second
Playback speed in frames per second.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.application.playback_fps.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPLICATION_PLAYBACK_FPSType:
intDefault:
10.
Playback loop mode
Loop mode for playback.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.application.playback_mode.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPLICATION_PLAYBACK_MODEType:
LoopModeDefault:
<LoopMode.LOOP: 'loop'>.
Save window geometry
Toggle saving the main window size and position.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.application.save_window_geometry.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPLICATION_SAVE_WINDOW_GEOMETRYType:
boolDefault:
True.
Save window state
Toggle saving the main window state of widgets.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.application.save_window_state.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPLICATION_SAVE_WINDOW_STATEType:
boolDefault:
False.
Full path to a startup script
Path to a Python script that will be executed on napari startup. This can be used to customize the behavior of napari or load specific plugins automatically.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.application.startup_script.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPLICATION_STARTUP_SCRIPTType:
PathDefault:
PosixPath('.').
Vertical Axis Orientation
Orientation of the vertical axis in 2D and 3D view. Default is “Down”.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.application.vertical_axis_orientation.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPLICATION_VERTICAL_AXIS_ORIENTATIONType:
VerticalAxisOrientationDefault:
<VerticalAxisOrientation.DOWN: 'down'>.
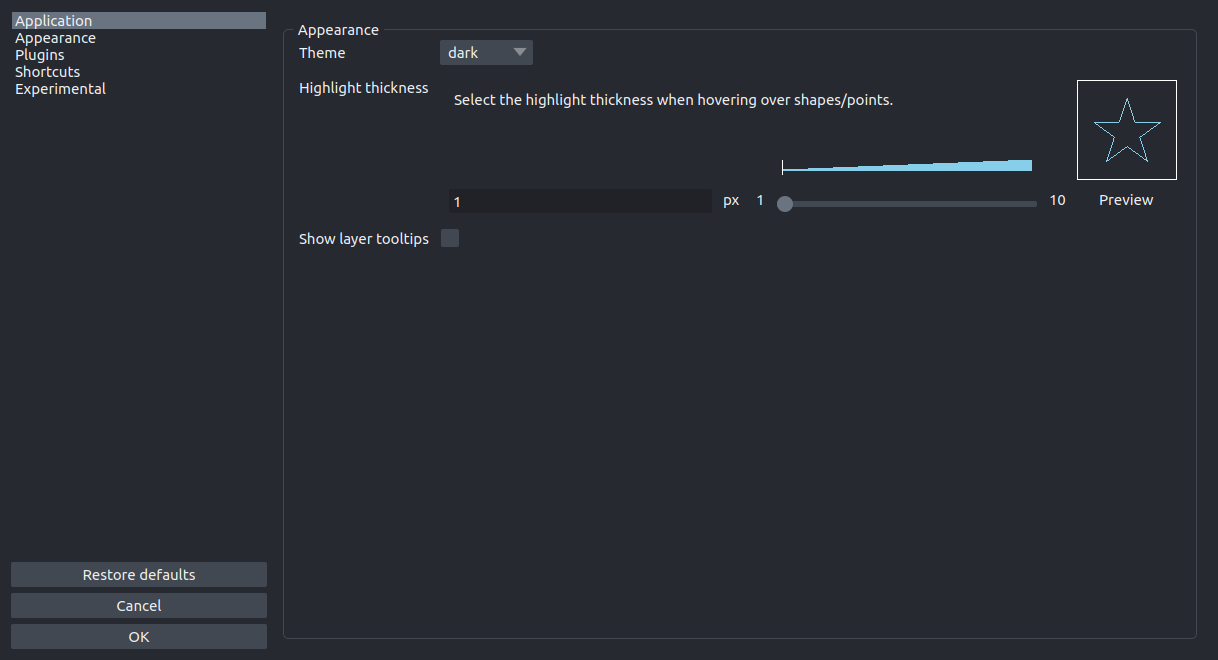
Appearance Settings#
User interface appearance settings.
More details on the individual Appearance settings
Font size
Select the user interface font size.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.appearance.font_size.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPEARANCE_FONT_SIZEType:
ConstrainedIntValueDefault:
9.
Highlight
Select the highlight color and thickness to use when hovering over shapes/points.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.appearance.highlight.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPEARANCE_HIGHLIGHTType:
HighlightSettingsDefault:
HighlightSettings(highlight_thickness=1, highlight_color=[0.0, 0.6, 1.0, 1.0]).
Show layer tooltips
Toggle to display a tooltip on mouse hover.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.appearance.layer_tooltip_visibility.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPEARANCE_LAYER_TOOLTIP_VISIBILITYType:
boolDefault:
False.
Theme
Select the user interface theme.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.appearance.theme.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPEARANCE_THEMEType:
ThemeDefault:
'dark'.
Update status based on layer
Calculate status bar based on current active layer and mouse position.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.appearance.update_status_based_on_layer.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_APPEARANCE_UPDATE_STATUS_BASED_ON_LAYERType:
boolDefault:
True.
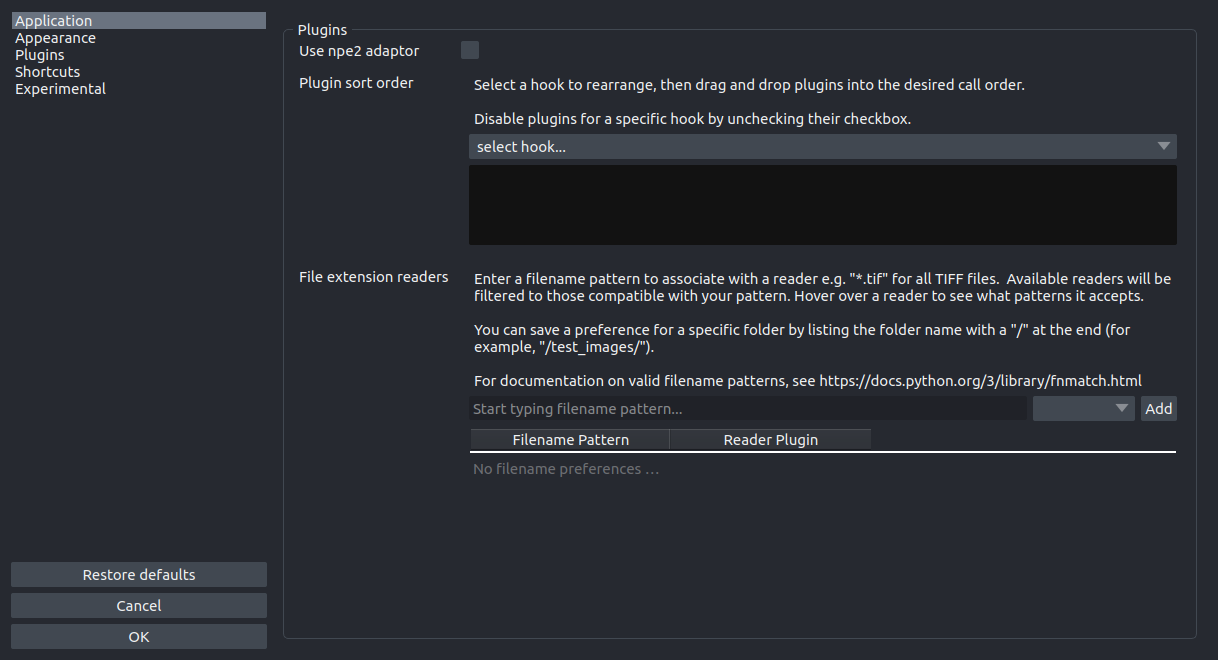
Plugins Settings#
Plugins settings.
More details on the individual Plugins settings
Plugin sort order
Sort plugins for each action in the order to be called.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.plugins.call_order.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_PLUGINS_CALL_ORDERType:
Mapping[str, list[napari.settings._plugins.PluginHookOption]]Default:
{}.
File extension readers
Assign file extensions to specific reader plugins
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.plugins.extension2reader.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_PLUGINS_EXTENSION2READERType:
Mapping[str, str]Default:
{}.
Only warn for new adapted plugins
Only warn about newly installed adapted plugins. Leave unchecked to receive warning with each startup.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.plugins.only_new_shimmed_plugins_warning.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_PLUGINS_ONLY_NEW_SHIMMED_PLUGINS_WARNINGType:
boolDefault:
False.
Use npe2 adaptor
Use npe2-adaptor for first generation plugins. When an npe1 plugin is found, this option will import its contributions and create/cache a ‘shim’ npe2 manifest that allows it to be treated like an npe2 plugin (with delayed imports, etc…)
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.plugins.use_npe2_adaptor.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_PLUGINS_USE_NPE2_ADAPTORType:
boolDefault:
True.
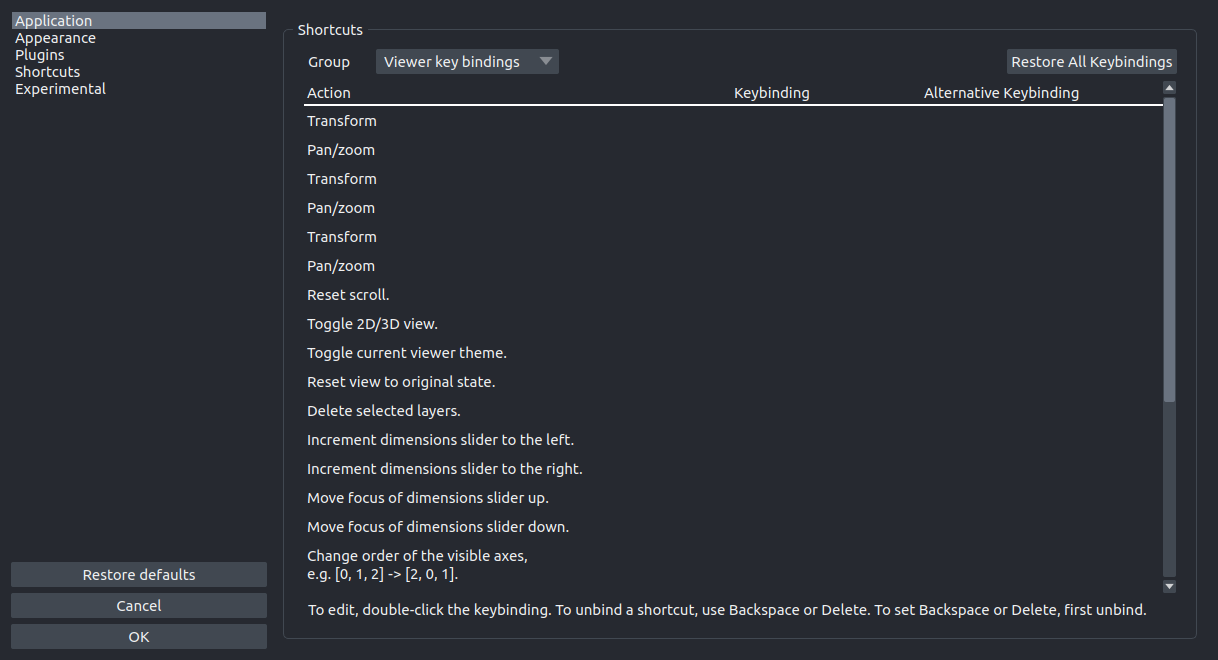
Shortcuts Settings#
Shortcut settings.
More details on the individual Shortcuts settings
shortcuts
Set keyboard shortcuts for actions.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.shortcuts.shortcuts.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_SHORTCUTS_SHORTCUTSType:
Mapping[str, list[app_model.types._keys._keybindings.KeyBinding]]
Default Shortcuts
Action |
Shortcut |
|---|---|
napari:toggle_console_visibility |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f334e930: Ctrl+Shift+C>] |
napari:toggle_ndisplay |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f334e8a0: Ctrl+Y>] |
napari:toggle_theme |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f334ecf0: Ctrl+Shift+T>] |
napari:reset_view |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f334ef00: Ctrl+R>] |
napari:delete_selected_layers |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f334ee10: Ctrl+Delete>, <KeyBinding at 0x7f84f334ede0: Ctrl+Backspace>] |
napari:show_shortcuts |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f47e3d40: Ctrl+Alt+/>] |
napari:increment_dims_left |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f47e3710: Left>] |
napari:increment_dims_right |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f53e2630: Right>] |
napari:focus_axes_up |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f89edf70: Alt+Up>] |
napari:focus_axes_down |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f8437f80: Alt+Down>] |
napari:roll_axes |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f8437f50: Ctrl+E>] |
napari:transpose_axes |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f8901ca0: Ctrl+T>] |
napari:rotate_layers |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f8902f00: Ctrl+Alt+T>] |
napari:toggle_grid |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f8903290: Ctrl+G>] |
napari:toggle_selected_visibility |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f8903f50: V>] |
napari:toggle_unselected_visibility |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f8903a40: Shift+V>] |
napari:select_layer_above |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f8902420: Ctrl+Up>] |
napari:select_layer_below |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f89030e0: Ctrl+Down>] |
napari:show_only_layer_above |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f8902600: Shift+Alt+Up>] |
napari:show_only_layer_below |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f8901520: Shift+Alt+Down>] |
napari:hold_for_pan_zoom |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f8902240: Space>] |
napari:activate_labels_erase_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f89018e0: 1>, <KeyBinding at 0x7f84f8900a40: E>] |
napari:activate_labels_paint_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f8901010: 2>, <KeyBinding at 0x7f84f8900e60: P>] |
napari:activate_labels_polygon_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f8900470: 3>] |
napari:activate_labels_fill_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f8903bf0: 4>, <KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891fdd0: F>] |
napari:activate_labels_picker_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891f8c0: 5>, <KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891f260: L>] |
napari:activate_labels_pan_zoom_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891e5a0: 6>, <KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891d8e0: Z>] |
napari:activate_labels_transform_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891caa0: 7>] |
napari:new_label |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891c110: M>] |
napari:swap_selected_and_background_labels |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891c860: X>] |
napari:decrease_label_id |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891c680: ->] |
napari:increase_label_id |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891d700: =>] |
napari:decrease_brush_size |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891cc80: [>] |
napari:increase_brush_size |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891d520: ]>] |
napari:toggle_preserve_labels |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891e3c0: B>] |
napari:reset_polygon |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891da30: Escape>] |
napari:complete_polygon |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891e210: Enter>] |
napari:activate_points_add_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891f020: 2>, <KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891e780: P>] |
napari:activate_points_select_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891ee70: 3>, <KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891f800: S>] |
napari:activate_points_pan_zoom_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891f3b0: 4>, <KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891f7d0: Z>] |
napari:activate_points_transform_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891fd10: 5>] |
napari:select_all_in_slice |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891f980: A>, <KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891fc80: Ctrl+A>] |
napari:select_all_data |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f891ff20: Shift+A>] |
napari:delete_selected_points |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f892cbf0: 1>, <KeyBinding at 0x7f84f892c620: Delete>, <KeyBinding at 0x7f84f892c0e0: Backspace>] |
napari:activate_add_rectangle_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f892c560: R>] |
napari:activate_add_ellipse_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f892c1a0: E>] |
napari:activate_add_line_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f892c4d0: L>] |
napari:activate_add_path_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f892cb60: T>] |
napari:activate_add_polyline_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f892c6e0: Shift+L>] |
napari:activate_add_polygon_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f892c9e0: P>] |
napari:activate_add_polygon_lasso_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f892cc20: Shift+P>] |
napari:activate_direct_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f8de3620: 4>, <KeyBinding at 0x7f84f8e21dc0: D>] |
napari:activate_select_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a5ac0: 5>, <KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a4ec0: S>] |
napari:activate_shapes_pan_zoom_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a5250: 6>, <KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a5460: Z>] |
napari:activate_shapes_transform_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a5610: 7>] |
napari:activate_vertex_insert_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a59a0: 2>, <KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a5d30: I>] |
napari:activate_vertex_remove_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a4c50: 1>, <KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a4b30: X>] |
napari:copy_selected_shapes |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a4770: Ctrl+C>] |
napari:paste_shape |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a4860: Ctrl+V>] |
napari:move_shapes_selection_to_front |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a4650: F>] |
napari:move_shapes_selection_to_back |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a4350: B>] |
napari:select_shapes_in_slice |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a4590: A>, <KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a4500: Ctrl+A>] |
napari:delete_selected_shapes |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a4050: 3>, <KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a43b0: Delete>, <KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a4170: Backspace>] |
napari:finish_drawing_shape |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a4a40: Enter>, <KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a6540: Escape>] |
napari:orient_plane_normal_along_x |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a4ad0: X>] |
napari:orient_plane_normal_along_y |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a4e30: Y>] |
napari:orient_plane_normal_along_z |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a5070: Z>] |
napari:orient_plane_normal_along_view_direction |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a52e0: O>] |
napari:activate_image_pan_zoom_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a5490: 1>] |
napari:activate_image_transform_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a56a0: 2>] |
napari:activate_vectors_pan_zoom_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a58e0: 1>] |
napari:activate_vectors_transform_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a5a90: 2>] |
napari:activate_tracks_pan_zoom_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a5d00: 1>] |
napari:activate_tracks_transform_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a5f70: 2>] |
napari:activate_surface_pan_zoom_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a6030: 1>] |
napari:activate_surface_transform_mode |
[<KeyBinding at 0x7f84f88a61e0: 2>] |
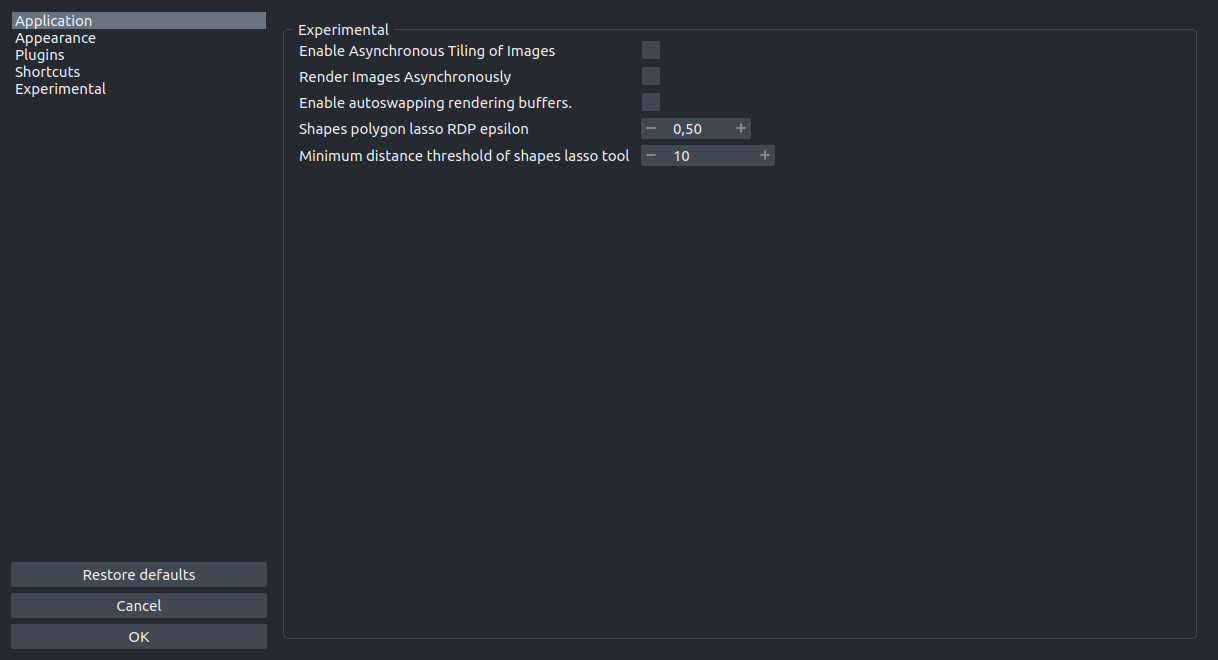
Experimental Settings#
Experimental settings.
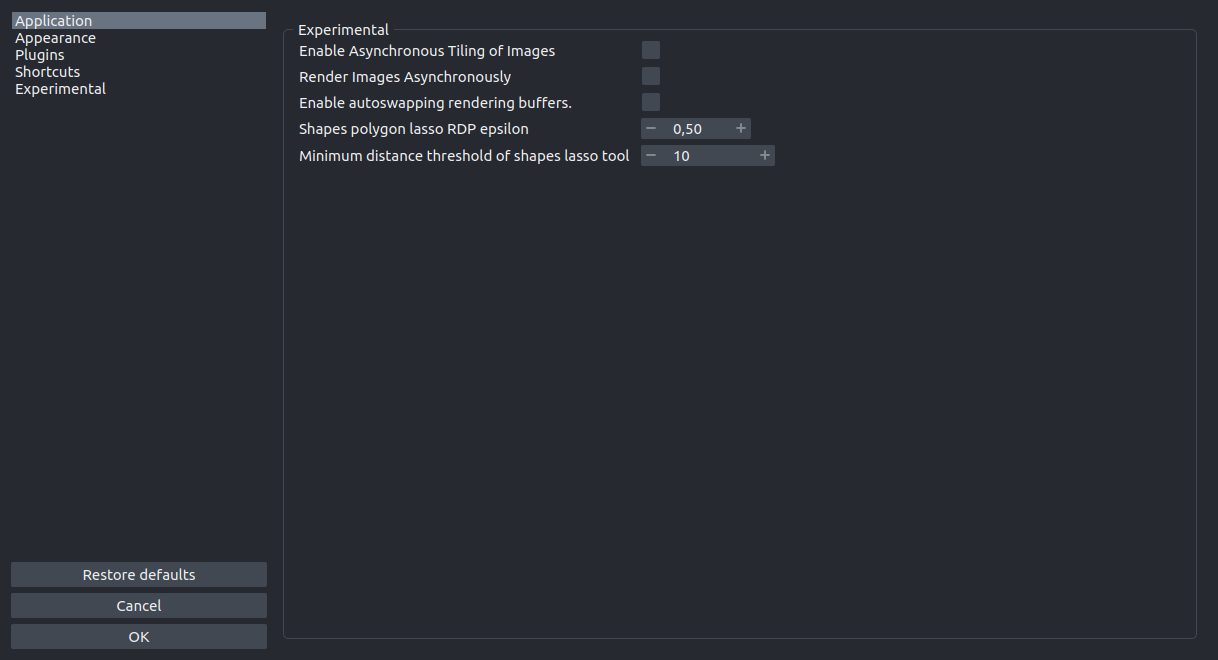
More details on the individual Experimental settings
Render Images Asynchronously
Asynchronous loading of image data. This setting partially loads data while viewing.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.experimental.async_.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_EXPERIMENTAL_ASYNC_Type:
boolDefault:
False.
Enable autoswapping rendering buffers.
Autoswapping rendering buffers improves quality by reducing tearing artifacts, while sacrificing some performance.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.experimental.autoswap_buffers.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_EXPERIMENTAL_AUTOSWAP_BUFFERSType:
boolDefault:
False.
Colormap backend to use for Labels layer
*Color mapping backend to use for Labels layer. ‘partsegcore’ requires the optional ‘partsegcore-compiled-backend’ package. ‘numba’ requires the optional ‘numba’ package. ‘pure python’ uses only NumPy and Python. The ‘fastest available’ backend will select the fastest installed backend. *
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.experimental.colormap_backend.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_EXPERIMENTAL_COLORMAP_BACKENDType:
ColormapBackendDefault:
fastest_available.
Double-click Labels polygon completion radius (-1 to always complete)
Max radius in pixels from first vertex for double-click to complete a polygon; set -1 to always complete.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.experimental.completion_radius.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_EXPERIMENTAL_COMPLETION_RADIUSType:
intDefault:
-1.
Minimum distance threshold of shapes lasso and path tool
Value determines how many screen pixels one has to move before another vertex can be added to the polygonor path.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.experimental.lasso_vertex_distance.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_EXPERIMENTAL_LASSO_VERTEX_DISTANCEType:
ConstrainedIntValueDefault:
10.
Shapes polygon lasso and path RDP epsilon
Setting this higher removes more points from polygons or paths. Setting this to 0 keeps all vertices of a given polygon or path.
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.experimental.rdp_epsilon.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_EXPERIMENTAL_RDP_EPSILONType:
ConstrainedFloatValueDefault:
0.5.
Triangulation backend to use for Shapes layer
*Triangulation backend to use for Shapes layer. The ‘bermuda’ requires the optional ‘bermuda’ package. The ‘partsegcore’ requires the optional ‘partsegcore-compiled-backend’ package. The ‘triangle’ requires the optional ‘triangle’ package. The ‘numba’ backend requires the optional ‘numba’ package. The ‘pure python’ backend uses the default Python triangulation from vispy. The ‘fastest available’ backend will select the fastest available backend. *
Access programmatically with
SETTINGS.experimental.triangulation_backend.Environmental variable:
NAPARI_EXPERIMENTAL_TRIANGULATION_BACKENDType:
TriangulationBackendDefault:
fastest_available.
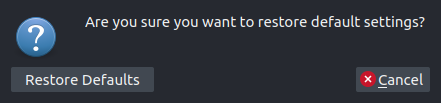
Reset settings to defaults using the Preferences dialog#
To reset the preferences click on the Restore defaults button and continue
by clicking on Restore Defaults.
Overriding settings#
napari settings can also be overridden by using environment variables.
The variable names follow a pattern: they start with NAPARI,
followed by the Preference section name, yielding, for example, NAPARI_APPLICATION, followed by the setting
name, yielding, for example, NAPARI_APPLICATION_CONFIRM_CLOSE_WINDOW.
(This specific setting controls whether napari will prompt you to confirm closing the application.)
You can also find the environmentvariable names for each setting in the descriptions for each of the Preference sections above.
You can override settings for a single napari session by setting environment variables at launch:
On Mac and Linux:
NAPARI_APPLICATION_CONFIRM_CLOSE_WINDOW=False napari
On Windows:
set NAPARI_APPLICATION_CONFIRM_CLOSE_WINDOW=False && napari
Or programatically in a script/notebook:
import os
os.environ['NAPARI_APPLICATION_CONFIRM_CLOSE_WINDOW'] = 'False'
Or, depending on your shell, you can persist environment variables for a shell session
using the export command (e.g. bash, zsh):
export NAPARI_APPLICATION_CONFIRM_CLOSE_WINDOW=False
Or, to persist between shell sessions, add the above command to your
shell configuration file e.g ~/.bashrc or ~/.zshrc.