Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Custom image interpolation kernels¶
When interpolation is set to ‘custom’, the convolution kernel provided by custom_interpolation_kernel_2d is used to convolve the image on the gpu. In this example, we use custom gaussian kernels of arbitrary size, a sharpening kernel and a ridge detection kernel.
Under the hood, this works by by sampling the image texture with linear interpolation in a regular grid (of size = of the kernel) around each fragment, and then using the weights in the kernel to add up the final fragment value.
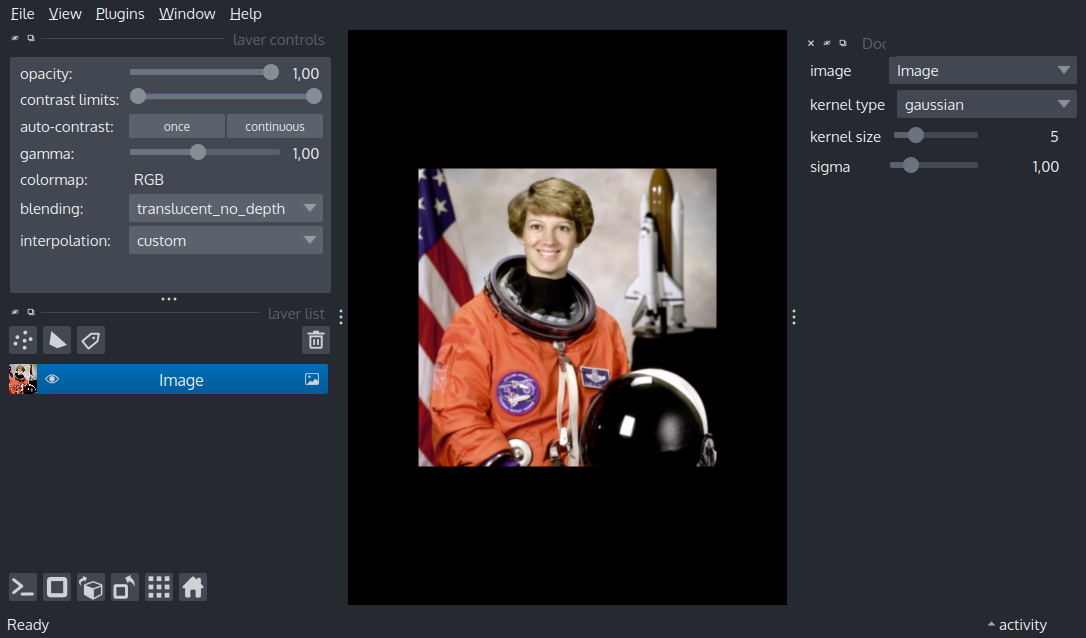
import numpy as np
from magicgui import magicgui
from scipy.signal.windows import gaussian
from skimage import data
import napari
viewer = napari.view_image(data.astronaut(), rgb=True, interpolation='custom')
def gaussian_kernel(size, sigma):
window = gaussian(size, sigma)
kernel = np.outer(window, window)
return kernel / kernel.sum()
def sharpen_kernel():
return np.array([
[ 0, -1, 0],
[-1, 5, -1],
[ 0, -1, 0],
])
def ridge_detection_kernel():
return np.array([
[-1, -1, -1],
[-1, 9, -1],
[-1, -1, -1],
])
@magicgui(
auto_call=True,
kernel_size={"widget_type": 'Slider', "min": 1, "max": 20},
sigma={"widget_type": 'FloatSlider', "min": 0.1, "max": 5, "step": 0.1},
kernel_type={"choices": ['none', 'gaussian', 'sharpen', 'ridge_detection']},
)
def gpu_kernel(image: napari.layers.Image, kernel_type: str = 'gaussian', kernel_size: int = 5, sigma: float = 1):
if kernel_type == 'none':
image.interpolation2d = 'linear'
else:
image.interpolation2d = 'custom'
if kernel_type == 'gaussian':
gpu_kernel.kernel_size.show()
gpu_kernel.sigma.show()
else:
gpu_kernel.kernel_size.hide()
gpu_kernel.sigma.hide()
if kernel_type == 'gaussian':
image.custom_interpolation_kernel_2d = gaussian_kernel(kernel_size, sigma)
elif kernel_type == 'sharpen':
image.custom_interpolation_kernel_2d = sharpen_kernel()
elif kernel_type == 'ridge_detection':
image.custom_interpolation_kernel_2d = ridge_detection_kernel()
viewer.window.add_dock_widget(gpu_kernel)
gpu_kernel()
if __name__ == '__main__':
napari.run()